What Track Maintenance Is and How It Still Employs People
Written by Chris, updated Jul 15 2019 in accordance with our editorial policy.
I used to work with (and still do occasionally) crews of people responsible for maintaining train lines. These crews specialise in maintaining the trains, the signals, or the tracks. I’m sharing here what track maintenance is, and what these crews get up to.
Track maintenance aims to keep trains running smoothly and at speed over track. To accomplish this, track maintenance means looking after the ballast, sleepers, and rails to ensure that any problems are identified and repaired before they can damage or derail trains.
By repairing and replacing the different components of rail track, track maintainers prevent the rails from falling out of shape. If the rails are straight - aligned horizontally and vertically - trains can travel over the tracks at speed without any risk of coming off the tracks.
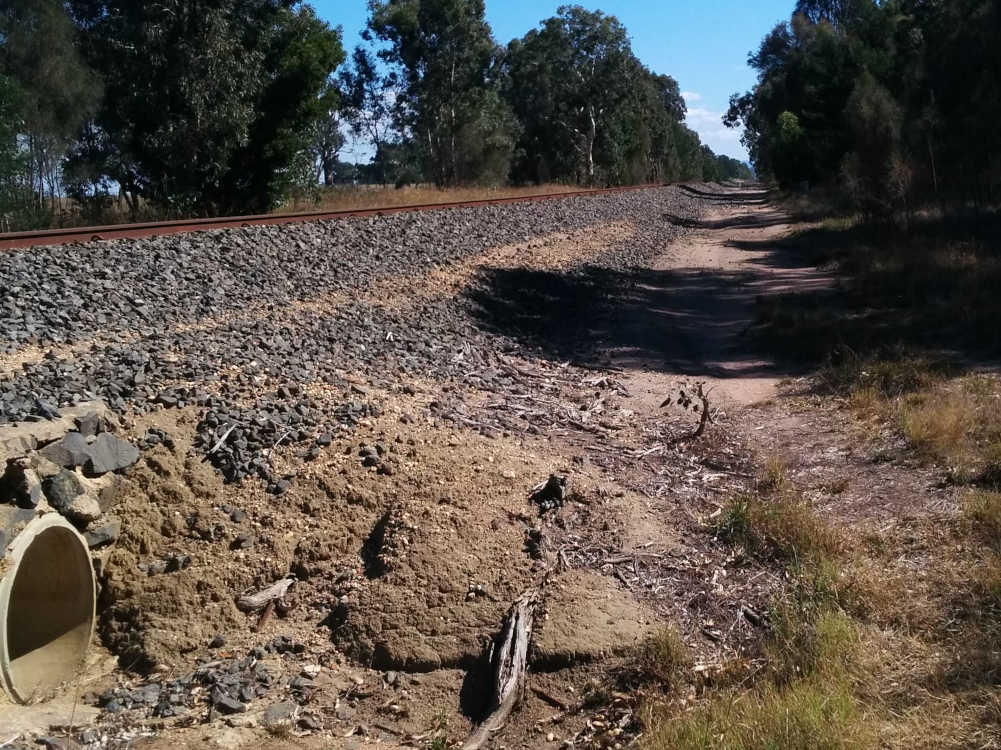 Rails, ballast, drainage: The key components looked after by track maintenance.
Rails, ballast, drainage: The key components looked after by track maintenance.
Why does track need to be maintained?
Safety.
To allow a train to run over track safely, the distance between the two rails must be right amount. Rails are held at this fixed distance apart by blocks of wood, concrete, or steel. These blocks are called sleepers or ties.
Tracks that sit on crushed rock, called ballast, need to have that crushed rock fixed up every so often. Due to rain washing it away, or from the movement of trains over the top, the rock can become uneven. When the rock becomes uneven, the rails become uneven, and this makes for a bumpy ride on the train.
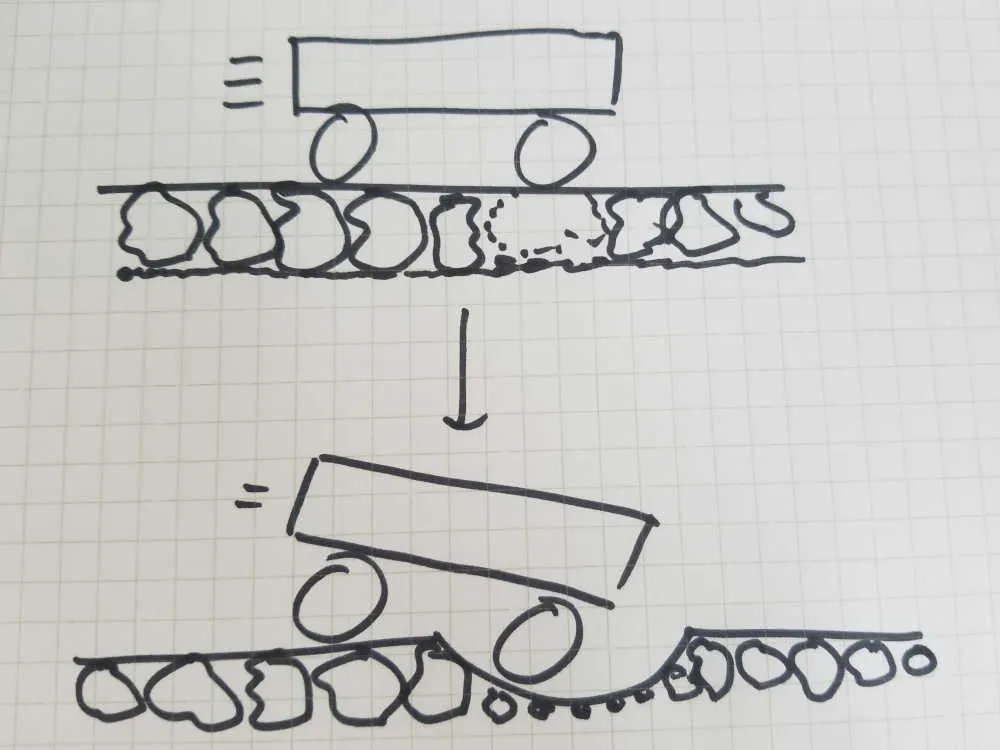 When ballast wears away, trains have a bumpy ride
When ballast wears away, trains have a bumpy ride
Each rail has a shape that matches the train wheel. As the wheels run over the rail they grind away at the rail and change its shape. Part of track maintenance is to grind the rail head back in to shape. If the rail develops a crack or a chip, it can damage train wheels. Maintaining the track is repairing the rails as well.
Looking after the track saves money. Trains damage their wheels, axles, and bodies when they run too fast over damaged track. Spending money repairing the track lets trains run faster, and saves money on repairing the trains.
Not looking after the train tracks can cause derailment. I analysed a few years worth of derailment data to find out why trains derail. The majority of cases were due to track and many caused by its lack of maintenance. Click here if you’re interested in finding out what else causes derailments and the consequences of trains coming off the tracks: https://econstructioncareers.com/news-insight/why-trains-derail
How are train tracks maintained and replaced?
Gaps can form in the rocks and material below the train tracks. The rails sink in to these gaps. When train wheels go over the rails that have sunk, the wheels bounce. This is uncomfortable for the train, and can damage the train wheels. Chips and cracks can also form in the rail due to weather, and the passage of heavy trains.
Maintaining and replacing track is about fixing these gaps, chips and cracks.
To fix gaps in the ballast a machine lifts up the rail and the sleepers and presses down the rocks to reduce the gaps. This is called tamping. Usually this process involves putting new rocks in.
To fix the chips on the rail you can grind the rail or replace it. When the rail is cracked, it has to be replaced.
To replace rail, the best way I’ve seen is to cut out the broken piece, including any sleepers. The broken piece is removed and a fresh piece assembled in a factory is dropped in. This new piece is then welded together. There are other ways of replacing broken rail, but this is the best I’ve seen.
Why is the train line closed when there is track maintenance?
Replacing a piece of rail is not a quick or easy task. Replacing or cleaning the crushed rock underneath the rails is not a quick or easy task.
The train line has to be closed so that workers can replace the rail, the sleepers, or the rocks that the rail sits on.
In some cases this can be done at night. Night work is avoided though because:
- In many areas, night workers get paid more so it’s cheaper to replace track during the day;
- It makes a lot of noise if people nearby are trying to sleep;
- There are only a few hours to work, some jobs take more time.
What else happens while the track is being maintained?
Leaves delay trains, leaves need to be removed from train lines.
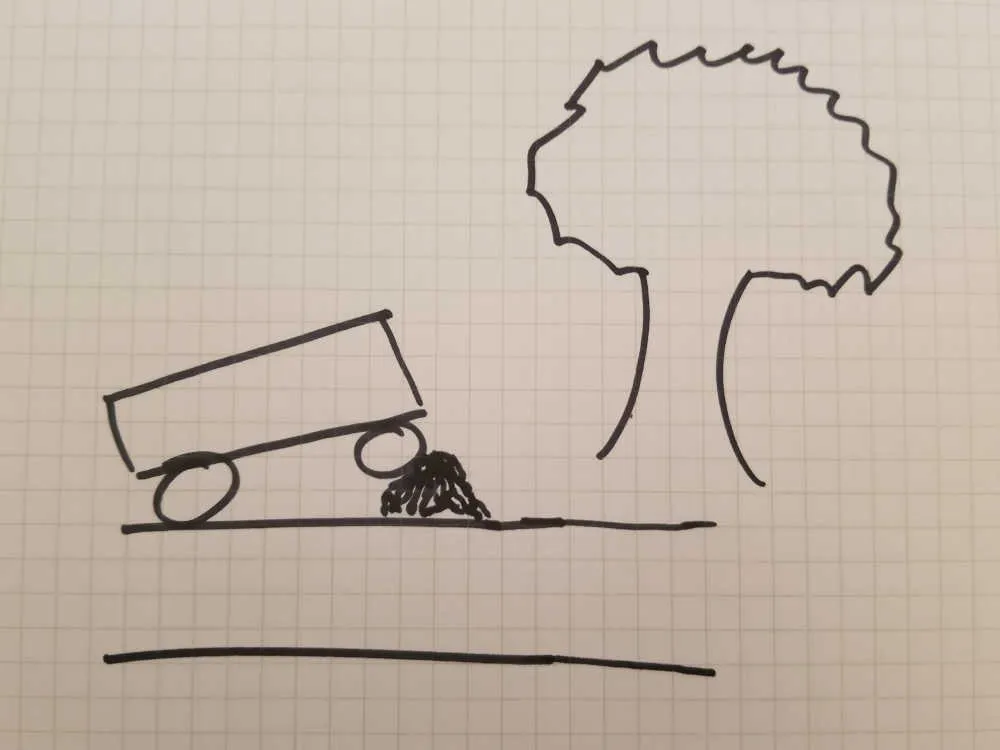 Wet leaves get stuck to the wheels of trains
Wet leaves get stuck to the wheels of trains
Why do leaves delay trains? Leaves prevent the wheels of the train gripping properly with the rails. This means trains struggle to stop properly when there are leaves on the tracks. The position of the train is also detected using the connection between the wheels and the rail. If the wheels aren’t sitting well on the rails, the train control computer doesn’t know where the trains are.
Leaves can be brushed or burnt off during track maintenance. Leaves also block drains.
Drains need to be cleared and allowed to flow. Allowing water to drain away from the tracks helps reduce the number of gaps that form in the ballast. Water can damage or wash away the crushed rock under the rails. Having clear drains is important to allow rain water to flow away without pooling and further damaging the crushed rock. Train drains need to be clear just as gutters on a house need to be cleared.
Greasing the rollers that allow trains to change track. There is a piece of rail that is switched to allow trains to change track. This piece of rail sits on rollers, and those rollers need to be maintained. The switching point is the cause of a lot of faults that rail operators blame on tracks or signals. I wrote recently about how trains change tracks, check it out here: https://econstructioncareers.com/news-insight/how-trains-change-track
What does a track maintenance worker do?
Inspect the track; repair the track; look after the ground the track sits on.
A track maintenance worker is responsible for inspecting the track to see if the rails are damaged, out of alignment, or if the sleepers holding the rails together need replacing. I remember when track maintenance workers would walk along the track at night to inspect the rails. Many rail lines I see now are switching to drones and laser detectors mounted on trains. This allows more automated detection of faults. Even with automatic detection, track maintenance workers still need to diagnose the problem, and repair it.
If there are any problems identified, track maintenance workers repair the problem. Repair can involve operating plant to move and replace the track or the ballast; repair can involve welding; repair can also involve breaking concrete and setting new concrete in place. Whatever the problem related to the track, or the bed the track sits on, track maintenance workers are there to fix it.
The ground around the track includes drainage and the bed the track sits on. Making sure these are working well helps prevent other problems arising in the track. Cleaning drains, for example, ensures that the erosion of ballast by rain is slowed.
Track maintenance workers make sure trains run smoothly and at speed across the tracks, and that the trains are not damaged by doing so.
What qualifications do you need to be a track worker?
Track maintenance workers vary from labouring and plant operation to professional engineering and project management.
If you don’t have a university background there are great opportunities for joining the rail industry is in plant operation. Plant continues to replace labour intensive jobs. Get a license and get involved.
If you are looking at university, the opportunities here are engineering based. That means an engineering degree, in civil, mechanical, or electrical engineering. Many rail operators and their contractors offer programs for graduate engineers to introduce them to what it means to work in rail.
To find out more about how to get involved in rail, I wrote previously in more detail about what jobs are available, what qualifications you should have, and how to apply. Click here to check that out: https://econstructioncareers.com/news-insight/rail-engineer-good-career
Track maintenance is a necessity of any working rail line. Despite advances in machinery, track maintenance still employs people to inspect the track, repair the track, and look after the ground the track sits on. Automation is coming to track maintenance, particularly to the manual jobs of inspecting the track. I see a bright future here however; if you’re looking to build a career in rail track maintenance is a great place to start: Operate plant to repair the track, get some welding experience, or get in on the engineering side to diagnose the root causes of problems and plan larger maintenance programs.